
A UNIFIL convoy near the border town of Naqoura, in southern Lebanon. (Credit: Mahmoud Zayyat/AFP)
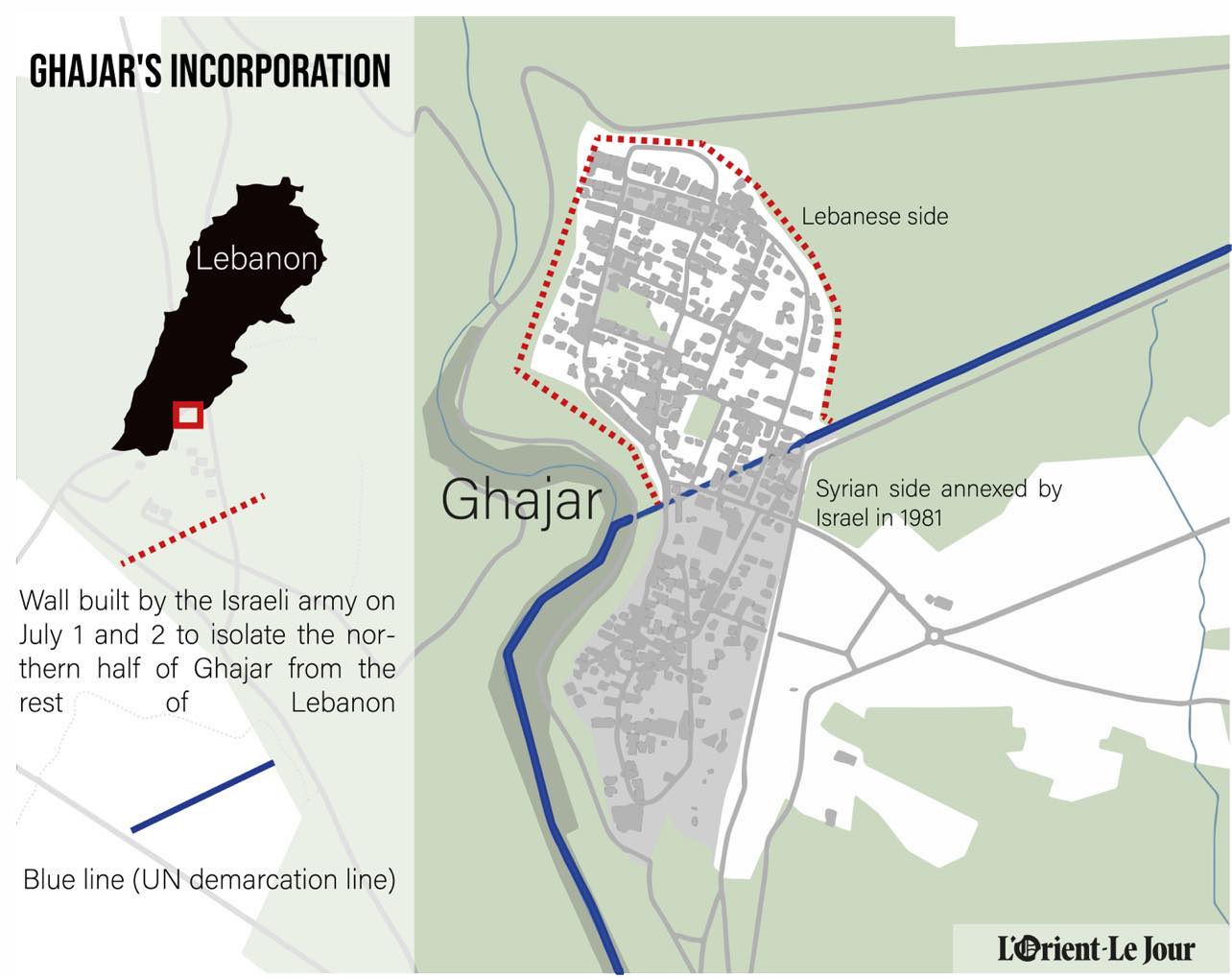
Over the weekend, Ghajar, a disputed village on the border between Lebanon and the occupied Syrian Golan Heights, was absorbed by Israel. The Israeli army constructed a fence to the north of the village, cutting it off from Lebanon.
The village, which is divided by the UN blue line, (the de-facto border between Lebanon and the Israeli-occupied portion of the Syrian Golan Heights) was occupied by Israel in the 2006 July war.
According to several experts, the property of the village is disputed between Lebanon, Syria, and Israel.
Who are the residents of Ghajar?
Some 2,000 people live in Ghajar. Most of the villagers still consider themselves Syrian Alawites, the minority sect which Syrian President Bashar al-Assad is part of. Many have taken Israeli citizenship during the long years of occupation and most residents refuse to be part of Lebanon.
How did Ghajar expand to Lebanon?
In 1967, Israel occupied the Syrian Golan Heights during the Six-day war. Residents who remained in Ghajar chose to accept Israeli citizenship when the territory was annexed in 1981. In 1982, when Israel occupied southern Lebanon, the village expanded into Lebanese territory. When Israel withdrew from southern Lebanon in 2000, the residents of northern Ghajar suddenly found themselves living in Lebanon, whilst their relatives and neighbors, who lived just across the street, now lived in a different country — an enemy state, separated by a fence.
The division of the village between Lebanon and Israel lasted until 2006, when Israel invaded north Ghajar during the July war.
In November 2022, Ghajar started allowing visitors and tourists from Israel after being a closed military zone for 22 years. Ghajar only allowed entry to visitors with special permission from the municipal council and the Israeli army.
In November 2010, Israeli cabinet approved a plan to withdraw from the northern part of the village, citing American concern and longstanding contention between Israel and Lebanon. Until this day however, Israel has not withdrawn from the village.
Other disputed areas claimed by Lebanon in the south, like Shebaa farms and Kafr Shuba hills, are still under Israeli occupation.
The village, which is divided by the UN blue line, (the de-facto border between Lebanon and the Israeli-occupied portion of the Syrian Golan Heights) was...
